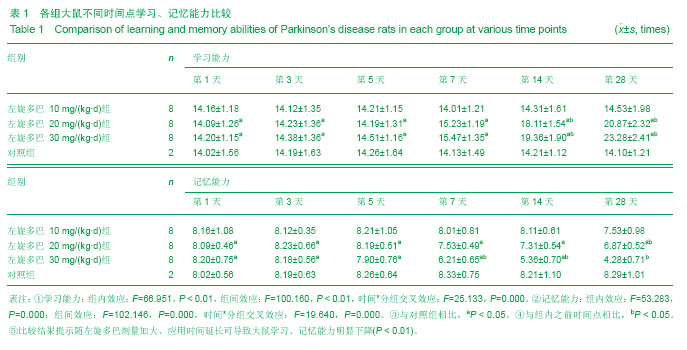
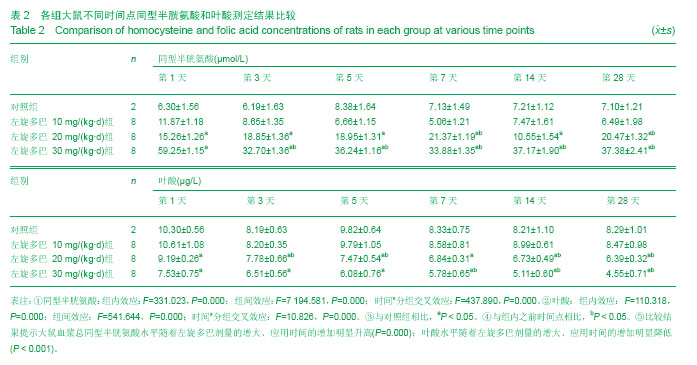
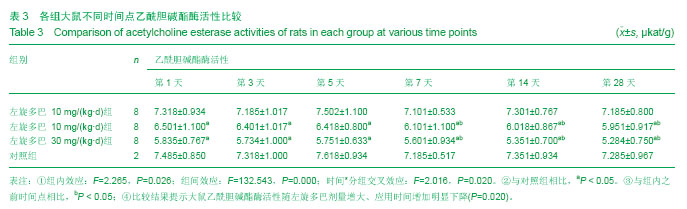
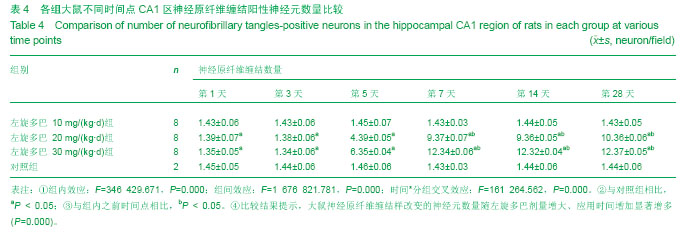
| [1] Wu N, Song L, Yang X, et al. NMDA receptor regulation of levodopa-induced behavior and changes in striatal G protein-coupled receptor kinase 6 and β-arrestin-1 expression in parkinsonian rats. Clin Interv Aging. 2013;8:347-352. [2] Muller T. Catechol-O-methyltransferase enzyme: cofactor S-adenosyl-L-methionine and related mechanisms. Int Rev Neurobiol. 2010;95:49-71. [3] Hooshmand B, Solomon A, Kåreholt I, et al. Associations between serum homocysteine, holotranscobalamin, folate and cognition in the elderly: a longitudinal study. J Intern Med. 2012;271(2):204-212. [4] Jellinger KA. Neurobiology of cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease. Expert Rev Neurother. 2012;12(12): 1451-1466. [5] Archibald NK, Hutton SB, Clarke MP, et al. Visual exploration in Parkinson's disease and Parkinson's disease dementia. Brain. 2013;136(Pt 3):739-750.[6] Zoccolella S, Lamberti SV, Iliceto G,et al. Hyperhomocysteinemia in L-dopa treated patients with Parkinson's disease: potential implications in cognitive dysfunction and dementia? Curr Med Chem. 2010;17(28): 3253-3261. [7] Thomas J, Wang J, Takuba H, et al. A 6-OHDA induced selective Parkinsonian rat model:further biochemical and behavioural characterization. J Exp Neurol. 1994;126:159-161.[8] Wang CF, Li DQ, Xue HY, et al. Oral supplementation of catalpol ameliorates diabetic encephalopathy in rats. Brain Res. 2010;1307:158-165. [9] Liu Y, Liu YQ, Morita T, et al. Effect of dietary supplementation with folate on choline deficiency-induced hyperhomocysteinemia in rats. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 2012;58(1):20-28.[10] Bonfanti G, Bitencourt PR, Bona KS, et al. Syzygium jambos and Solanum guaraniticum Show Similar Antioxidant Properties but Induce Different Enzymatic Activities in the Brain of Rats. Molecules. 2013;18(8):9179-9194. [11] Vallet PG, Guntern R, Hof PR, et al. A comparative study of histological and immunohistochemical methods for neurofibrillary tangles and senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1992;83(2):170-178. [12] Guatteo E, Yee A, McKearney J, et al. Dual effects of L-dopa on nigral dopaminergic neurons. Exp Neurol. 2013;247:582-594. [13] Pandey S. Parkinson's disease: recent advances.J Assoc Physicians India. 2012;60:30-32. [14] Smith GA, Heuer A, Dunnett SB, et al. Unilateral nigrostriatal 6-hydroxydopamine lesions in mice II: predicting L-dopa -induced dyskinesia. Behav Brain Res. 2012;226(1):281-292. [15] MullerT, HefterH, Hueber R, et al. Is levodopa toxic? J Neurol. 2004; 251(Suppl6): S44.[16] Jenner P. Avoidance of dyskinesia: preclinical evidence for continuous dopaminergic stimulation. Neurology. 2004;62 (1 Suppl 1):S47-55.[17] Sanders LH, Timothy Greenamyre J. Oxidative damage to macromolecules in human Parkinson disease and the rotenone model. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013;62:111-120. [18] Zuo L, Motherwell MS. The impact of reactive oxygen species and genetic mitochondrial mutations in Parkinson's disease. Gene. 2013;532(1):18-23. [19] Perier C, Bender A, García-Arumí E, et al. Accumulation of mitochondrial DNA deletions within dopaminergic neurons triggers neuroprotective mechanisms. Brain.2013;136(Pt 8): 2369-2378.[20] 王红梅,葛许华,周联生,等.帕金森病患者左旋多巴治疗对血浆同型半胱氨酸的影响[J].中华神经科杂志,2006,39(9): 609-611. [21] Shin JY, Ahn YH, Paik MJ,et al. Elevated homocysteine by levodopa is detrimental to neurogenesis in parkinsonian model. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50496.[22] Ganapathy PS, White RE, Ha Y, et al. The role of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor activation in homocysteine-induced death of retinal ganglion cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52(8):5515-5524.[23] Liu HH, Shih TS, Huang HR, et al. Plasma homocysteine is associated with increased oxidative stress and antioxidant enzyme activity in welders. Scientific World J. 2013;2013: 370487.[24] Zanin RF, Bergamin LS, Braganhol E, et al. Homocysteine modifies extracellular ATP availability in macrophages. Toxicol Vitro. 2013;27(8):2273-2278.[25] Scherer EB, Schmitz F, Vuaden FC, et al. Mild hyperhomocysteinemia alters extracellular adenine metabolism in rat brain. Neuroscience. 2012;223:28-34.[26] Kolling J, Scherer EB, Siebert C, et al. Homocysteine induces energy imbalance in rat skeletal muscle: Is creatine a protector? Cell Biochem Funct. 2013;31(7):575-584.[27] Vacek TP, Kalani A, Voor MJ, et al. The role of homocysteine in bone remodeling. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2013;51(3): 579-590.[28] Wang J, Bai X, Chen Y, et al. Homocysteine induces apoptosis of rat hippocampal neurons by inhibiting 14-3-3ε expression and activating calcineurin. PLoS One. 2012; 7(11): e48247. [29] Mattson MP, Shea TB. Folate and homocysteine metabolism in neural plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. Trends in Neurosci.2003;26(3): 137-146.[30] Aarsland D, Kurz MW. The epidemiology of dementia associated with Parkinson disease. Brain Pathol. 2010;20(3): 633-639.[31] Rana AQ, Yousuf MS, Naz S, et al. Prevalence and relation of dementia to various factors in Parkinson’ s disease. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2012;66(1): 64-68.[32] Hobson P, Meara J. Risk and incidence of dementia in a cohort of older subjects with Parkinson’s disease in the U-nited Kingdom. Mov Disord. 2004;19(9): 1043-1049.[33] Muslimovic D, Post B, Speelman JD, et al. Cognitive profile of patients with newly diagnosed Parkinson disease. Neurolgy. 2005;65:1239-1245.[34] Levy G, Tang MX, Louis ED, et al.The association of incident dementia with mortality in PD. Neurology. 2002;59: 1708- 1713.[35] Hutchinson M, Fazzini E. Cholinesrerase inhibition in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1996;61: 324-325.[36] 乔晋,屈秋民,郭峰,等.55岁以上自然人群中帕金森病患者认知功能障碍的临床研究[J].西安交通大学学报,2004,2(25):100-104.[37] Anand P, Singh B. A review on cholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer's disease. Arch Pharm Res. 2013;36(4): 375-399. [38] Tajes M, Guivernau B, Ramos-Fernández E, et al. The pathophysiology of triose phosphate isomerase dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease. Histol Histopathol. 2013;28(1):43-51.[39] Krüger U, Wang Y, Kumar S, et al. Autophagic degradation of tau in primary neurons and its enhancement by trehalose. Neurobiol Aging. 2012;33(10):2291-2305.[40] Allam M, Fahmy E, Elatti SA,et al.Association between total plasma homocysteine level and cognitive functions in elderly Egyptian subjects. J Neurol Sci. 2013;332(1-2):86-91. [41] 夏霁摘.血浆同型半胱氨酸是老年性痴呆的危险因素[J]. 国外医学:卫生学分册, 2002, 21(3): 7-8. |
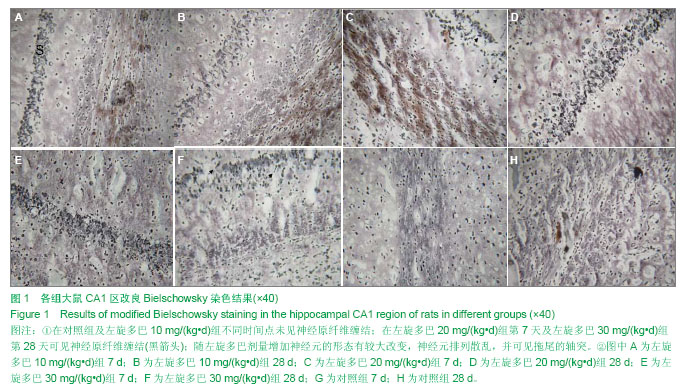
.jpg)